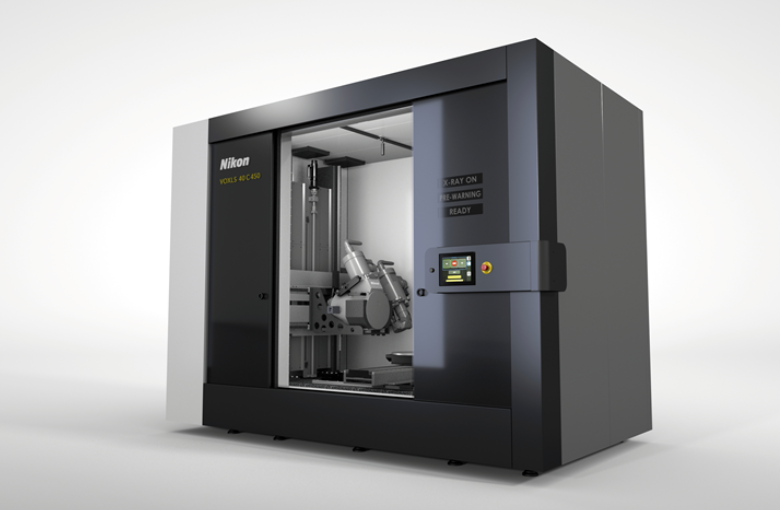
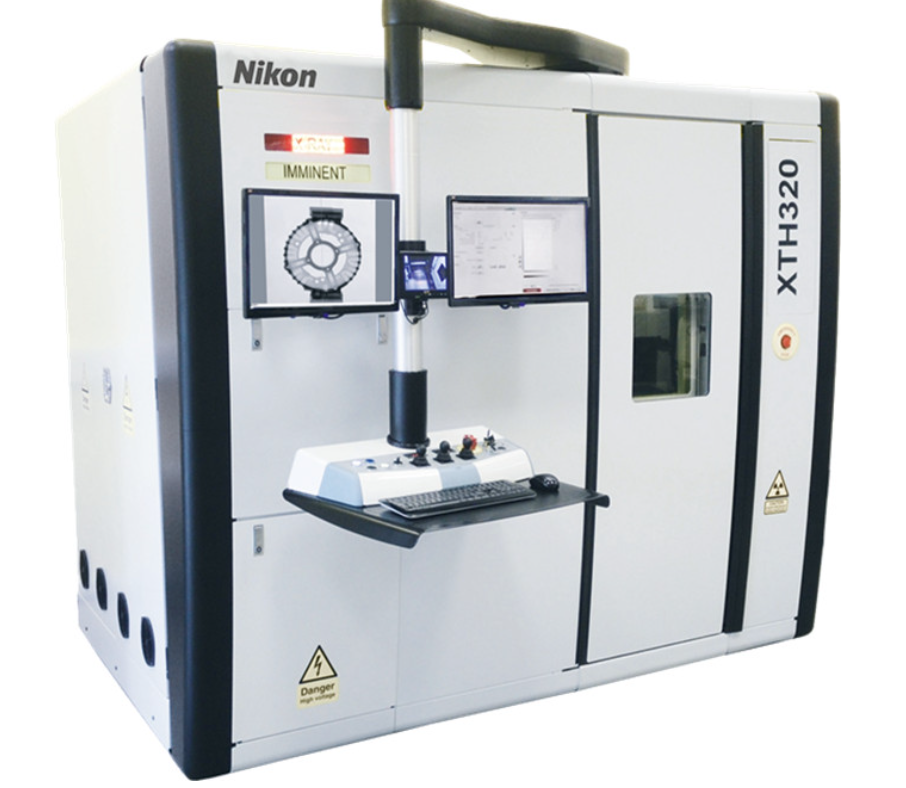
Composite workpieces require various controls and inspections during the overall production process. Computed tomography (CT) is a powerful non-destructive technology to inspect every sample in an easy way and the only one giving the ability to see inside the matter.
Composites components are diverse and widely used in various industrial fields such as the aerospace, automotive or naval industries. They have complex material behavior displaying a range of failure modes. Composites and fiber materials have an internal structure, that depending on the length of the single fiber and the manufacturing process can be random or periodic. The structure combined with the properties of the fibers and the matrix determines the mechanical behavior of the component.
Characterize Fibers Features Exploring The Matrix Structure
Industrial CT scanning technology is the only inspection technique able to characterize, in an easy way, the overall material structure of a composite component. CT can provide precise measurements of the overall sample, from the whole structure down to individual fiber level. Every structural and dimensional aspect of composite parts can be assessed through one CT dataset. Computed tomography is an effective device to create models for prediction of the mechanical properties of composites.
Industrial CT scanning allows quick and accurate inspection of parts’ internal and external structures. With high resolution CT devices enable the validation of tiny details on composite components. It is possible to define and export an accurate 3D model of the sample to make measurements of the inner and outer geometries, on simple or multi-material parts.
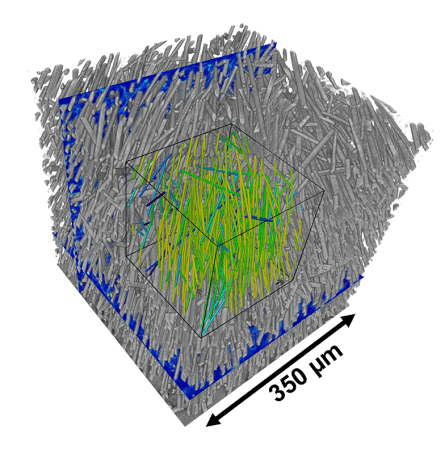
CT datasets contain the entire sample geometric information and can be used to perform different kinds of analyses: voids analysis, actual parts to CAD comparison, part to part comparison, wall thickness analysis or reverse engineering. A large number of parameters can be quantified: local and global fiber orientation, local and global fiber concentration, deviation from predefined reference orientation and other statistical parameters as fibers distribution.
Powerful Softwares Perform Advanced Analysis To Qualify Smallest Component Details
Industrial CT scanning technology provides the possibility to quantify the fiber orientation and distribution inside of components. It provides important information, since the distribution affects the mechanical and physical properties of the workpiece, such as its strengths, internal stress or fatigue properties. Powerful analysis software enables to know if the fiber distribution is isotropic and homogeneous, by representing every fiber as a tensor.

Furthermore, a comparison between a CT dataset and a CAD nominal file can be made easily, to quickly and accurately compare the part to CAD model, by showing the internal fibers deviations. Most advanced softwares combine the segmentation of the resulting 3D volume down to individual fibers, identification of the fiber orientation and length with classification of the fibers and fibers region.
Industrial CT scanning technology allows the identification of cracks, porosities or inclusions inside the scanned part. The volume fraction of pores and their spatial distribution in the sample can be calculated and highlighted with different colors using post-processing software.






















